Refractive errors arise from the misfocusing of light in the eye. Below are the four most common causes of blurred vision - all of these can be corrected by our optometrist with prescription glasses or contact lenses, so you can see clearly again.
myopia
also called 'near-sightedness or 'short-sightedness'
近視
|
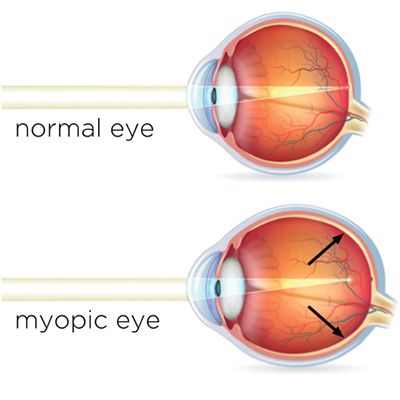
Myopia is commonly caused by the eye growing slightly too long, so light is mis-focused in front of the retina. The longer the eyeball, the greater the degree of myopia. Myopia typically begins in childhood and worsens in adolescence as the eye grows.
|
A person with myopia can see close objects clearly, while objects in the distance will appear blurry. A child with myopia may find it hard to see the board at school, while an adult may have trouble seeing signs when driving, or recognising faces from a distance.
|
Myopia development is influenced by both genetics and environmental factors. Having one or both parents with myopia, and spending a lot of time indoors, reading too close, school work, tablet and computer use all increase the risk of developing myopia.
|
Myopia is the most common vision problem in children and young adults.
And it poses the greatest risks for the long-term health of the eyes.
hyperopia
also called 'far-sightedness or 'long-sightedness'
近視
|
Hyperopia occurs when the eye is too short. Low amounts of hyperopia is common in kids and usually isn't a problem as children's eyes can adjust focus to compensate. However, some children may experience discomfort and headaches from the constant focusing.
|
A far-sighted person has better vision in the distance than at near. They need to work their eyes harder to focus up close, and to maintain that focus. Over time this causes the eye muscles to strain, often leading to headaches, sore eyes and tiredness.
|
Symptoms of hyperopia may be relieved by glasses, eye exercises or taking more breaks from close-up work. In children, a high degree of uncorrected hyperopia, particularly if only in one eye, can cause eye mis-aligment (strabismus) and lazy eye (amblyopia).
|
astigmatism
sometimes also called 'cylinder' or 'football shaped eye'
散光
|
Astigmatism is an irregularity or imperfection of the front surface of the eye. Instead of being perfectly round, the eye is oval shaped. Astigmatism is very common - around half of people with glasses have some amount of astigmatism in their glasses prescription.
|
People with astigmatism can have blurred vision in the distance as well as close-up. Some describe the blur as being like an overlapping shadow, which is very uncomfortable for the visual system. Astigmatism, when not corrected properly, can often cause headaches and eyestrain.
|
Astigmatism can occur alone or in combination with nearsightedness and farsightedness. Most types and degrees of astigmatism can be corrected fully by glasses and contact lenses. Contact lenses for astigmatism are often referred to as 'toric lenses'.
|
presbyopia
the loss of focusing flexibility with age
老花眼
|
As we age, our eyes gradually lose flexibility like the rest of our bodies. The lens inside our eyes becomes less elastic and less able to quickly adjust focus. Changing our focus from distance to near, and back, becomes slower. Reading and detailed close-up work becomes increasingly harder.
|
People with normal distance vision will start to hold their book further away to read more comfortably. Those who are naturally near-sighted may find close reading easier without their long-distance glasses. And farsighted people will find reading at near very difficult and uncomfortable.
|
Presbyopia tends to occur at around age 45, earlier for some and later for others. Prescription reading glasses will help. Those already wearing glasses for distance, multifocal or bifocal lenses may be the best solution to correct both the long and short distances in a single pair of glasses.
|
For clear and comfortable vision have your eyes tested.
By our experienced optometrist.
Eyecare Concepts | The Myopia Clinic © 2017-23
KEW EAST | MELBOURNE
KEW EAST | MELBOURNE